
Write the subshell electronic configuration of the following
elements?
- Helium
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Copper
- Chromium
- Fluorine
- Sulphur
(Atomic number of He-2, K – 19, Mg- 12, Fe- 26, Cu- 29,
Cr- 24, F- 9, S- 16)
Answers:
1.

Peculiarity of the subshell electronic configuration of
chromium and copper
In the electronic configuration of chromium and copper, the
outermost s orbit has one electron only. Why?
The d subshell can accommodate a maximum of 10 electrons.
The completely filled configuration (d10) or the half filled
configuration (d5) of this subshell is more stable than the others.
So the d4 s2 configuration
of chromium is changed to d5 s1 and the d9 s2
of copper is changed to d10 s1 .
Electronic configuration and block
The block to which an element belongs will be the same as
the subshell to which the last electron is added.
In the periodic table the first two groups belong to s
block, the groups from 13 to 18 belong to the p block and the groups from 3 to
12 belong to the d block. The elements at the bottom of the periodic table in
two separate rows (lanthanones and actinones) belong to f block.
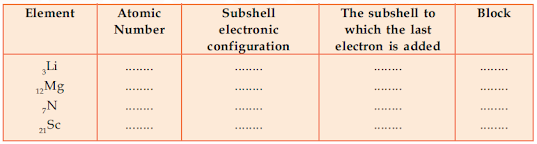
From the following electronic configuration identify the
block of each element.

Answer:


Subshell electronic configuration and group number.
Group number of s block elements
For s block elements the number
of electrons in the outermost subshell will be the group number.

Characteristics of p block elements
Metals, non-metals, metalloids and
all the noble gases are in this block.
Elements in the solid, liquid and
the gaseous state at room temperature are seen in this block.
p block elements usually show
higher ionisation energy than s block elements.
The element having the highest
electronegativity (fluorine) is in this block.
There are electropositive and
electronegative elements in this block (eg: Boron, Aluminium etc. are
electropositive elements, Oxygen, Chlorine etc. are electronegative elements).
Group number of d block elements

Characteristics of d block elements
d block elements are found in
groups 3 to 12 of the periodic table.
d block elements are known as transition
elements.
d block elements are metals.
The last electron is filled in the
d subshell of the penultimate shell.
They show variable oxidation
state.
They form coloured compounds.
Transition elements
Transition elements (d block elements) show similarities
in properties not only in groups but also in periods. Why?
The outermost subshell electronic configuration of
the transition elements are generally the same in a group and also along a
period, therefore they show similarities in properties not only in groups but
also in periods.
Transition elements show variable oxidation states. Why?
In the case of transition elements the difference in energy
between the outermost s subshell and the penultimate d subshell
is very small. Hence under suitable conditions the electrons in d
subshell also take part in chemical reactions. Hence transition elements
show variable oxidation states.
Most of the coloured salts are compounds of transition
elements. Why?
Most of the coloured salts are compounds of transition
elements. The colour is due to the presence of transition metal ions present in
these compounds.
Transition metal compounds and colours
Copper sulphate – blue
Cobalt nitrate – red brown
Potassium permanganate – dark
purple
Ferrous sulphate – green
Potassium dichromate – orange
Cobalt chloride – sky blue
Inner transition elements
f block elements
The f block elements are the elements
coming after lanthanum(6th period) and actinium(7th
period) and are placed in two rows at the bottom of the periodic table.
The elements in first row are
called lanthanoids and those in the second row are called actinoids.
Characteristics f block elements
These elements show variable
oxidation states
Most of the actinoids are
radioactive and are artificial elements.
f block elements Uranium, Thorium,
and Plutonium are used as fuels in nuclear reactors.
Many of f block elements are used as catalyst in the petroleum industry.
Let's assess Questions and Answers





Ans:
Wrong electronic
configurations are a, c, and d





Ans:
a) 2d and 3f are not possible.
Extended activities Questions and Answers

Answers:

a) Halogens
b) -1
c) Flourine
d) Flourine
e) Some examples of compounds of halogens and s block
elements : NaF, NaCl, KF, KCl, MgF2 , MgCl2, CaF2



.png)

.png)

.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)






0 Comments