.jpg)
Complete the table given below.


Let's Assess
1. A chain having 6 carbon atoms is given below.

a) Complete the structure by adding hydrogen atoms to each carbon atom.
Ans:

b) Write the molecular formula of this compound.
Ans: C₆H₁₄
c) How many carbon atoms are there in the main chain of this compound?
Ans: 5
d) Write its IUPAC name.
Ans:3-Methylpentane
2. Write down the IUPAC names of the given compounds.


Ans:
a) 3-Methylhexane
b) Hex-2-ene
c) Hex-2-yne
d) Pentanoic acid
e) Butanal
f) Pentan-2-one
g) 2, 2-Dichlorobutane
h) Ethoxyethane
i) 3-Methylbut-2-ene
j) 3-Methylbut-1-yne
3. Write the structural formulae of the compounds given below.
a) 2,3,3–Trimethylhexane
Ans:

b) Ethoxybutane
Ans:

c) Butan-2-one
Ans:

d) Pent–1–yne
Ans:

e) Hexan–2–ol
Ans:
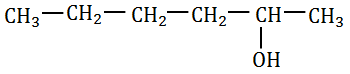
f) 3–Bromoheptane
Ans:

g) Pentanal
Ans:

4. The structural formulae and IUPAC names of certain compounds are given. Identify the wrong ones and correct them.

Ans: iii and iv are wrong.
Correct IUPAC names of the compounds are,
iii) Hex-2-yne
iv) 2,2,3-Trichloropentane
5. 

a) What type of isomerism do these compounds exhibit?
Ans: Functional Isomerism
b) Write the structural formula of the metamer of compound (i).
6. The structural formulae of two compounds are given.

a) What is the IUPAC name of the first compound?
Ans: Pentanal
b) These two compounds are isomers. Why?
Ans: Because they have the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
c) What type of isomerism do these compounds exhibit?
Ans: Functional isomerism
d) Write the structural formula of the position isomer of the second compound.
Ans:
7. Examine the compounds given below and identify the isomeric pairs. What type of isomerism is shown by each pair?
a) Methoxypropane
b) 2,3–Dimethylbutane
c) Propan–1–ol
d) Ethoxyethane
e) Propan–2–ol
f) Hexane
Ans:
a and d are metamers.
b and f are chain isomers.
c and e are position isomers.



.png)

.png)

.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)






0 Comments