
Fill three-fourth of a trough with water. Add two or three drops of milk into it. Cover the trough with a transparent sheet of paper. Fill the remaining space in the trough with smoke. Then flash the light from a laser torch as shown in figure and observe the path of light.

Air and Water
2) How will the path of light ray be, when it passes through only one medium?
The light ray will travel in a straight line without any deviation.
3) Is there any deviation in the direction of the ray of light when it enters obliquely from one medium to another?
Yes, the ray deviates from its path.
4) Where does the ray of light undergo a change in direction?
The ray undergoes a deviation at the surface of separation between the
mediums.
Allow light from a laser torch to fall perpendicular to the surface of the water taken in the trough.

5) Is there a deviation in the path of the ray of light?
No deviation in the path.
When light travels through a single medium, the path of light will be a straight line. A ray of light undergoes a deviation at the surface of separation when it enters obliquely from one medium to another. There will be no deviation in the path of the ray of light incident normally.
What causes a deviation in the path of the light ray?
Observe the speed and direction of a toy car moving from a smooth surface to a rough surface.

6) Is there a change in the direction of motion of the car?
Yes, the direction of motion of the car changes.
7) Where does this change occur?
At the boundary separating the rough surface from the smooth surface.
8) Did the car move with the same speed on both surfaces?
No, the speed on the rough surface is less than that on the smooth surface.
9) What causes the change in direction of the car?
The change in direction is caused by the change in the speed of the car as it
moves from one surface to the other.

The table shows the speed of light through various mediums. The speed of light is different in different mediums.
- The change in the speed of light causes the change in the direction of the ray of light, when it passes from one medium to another.
- The speed of light differs in various mediums due to the difference in their optical densities.
- The ability of a medium to influence the speed of light through the medium is its optical density.
- The speed of light will be lower in a medium of higher optical density (optically denser medium). The speed of light will be higher in a medium of lower optical density (optically rarer medium).
Arrange the mediums in the table in the increasing order of their optical densities.

Refraction
When a ray of light enters obliquely from one medium to another of different optical densities, it undergoes a deviation at the surface of separation of the mediums. This phenomenon is refraction.
Refractive index
Speed of light in vacuum (c) = 3 x 10⁸ m/s
10) The speed of light in different mediums is given in the table below. Find the refractive index of each medium and complete the table.
11) If the refractive index of diamond is 2.4, what is the speed of light that passes through it?

12) How is the speed of light related to refractive index?
The speed of light is less in a medium of higher refractive index.
13) How optical density is related to refractive index?
The speed of light is less in a medium of higher optical density.
Difference in the deviation of light when it enters from air to water and from water to air

Figure 1.7 (a)

The ray falling on the surface of separation of the two mediums is the incident ray.
The ray which undergoes refraction is the refracted ray.
The angle between refracted ray and the normal (NN') is the angle of refraction.
The angle between incident ray and the normal (NN') is the angle of incidence.
Find the incident ray, refracted ray, angle of incidence and angle of refraction from each figure and complete the table.

14) How does the direction of light change when a ray of light enters obliquely from air to water?
(deviates towards the normal / deviates away from the normal)
Ans: deviates towards the normal
15) How does the direction of light change when a ray of light enters obliquely from water to air?
(deviates towards the normal / deviates away from the normal)
Ans: deviates away from the normal
Observe the figures that show light passing through different pairs of mediums.

a) Which are the figures in which the ray of light enters obliquely from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium?
Ans: fig 1.8(b) & fig 1.8(d)
b) In this case, to which direction does the refracted ray deviate?
(towards the normal / away from the normal)
Ans: away from the normal
c) Choose the figures in which the refracted ray deviates towards the normal.
Ans: fig 1.8(a) & fig 1.8(f)
d) In which situation will a ray of light deviate towards the normal as it passes from one medium to another?
(from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium/from an optically rarer medium to a denser medium)
Ans: from an optically rarer medium to a denser medium
e) There is no refraction of light in figures 1.8 (c) and 1.8 (e). What may be the reason?
- When light enters from one medium to another, the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence, will be on the same plane.
- When light enters from an optically rarer medium to a denser medium, it deviates towards the normal.
- When light enters from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium, it deviates away from the normal.
- A ray incident normally at the surface of separation of mediums does not undergo refraction.
Refraction in a glass slab
Allow light from a laser torch to fall on a glass slab as shown in the figure.
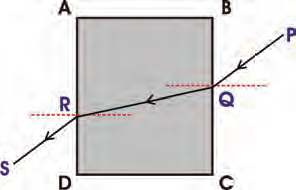
At which points do refraction occur for the ray of light?
Ans: At R & Q.
Allow light to incident normally on the glass slab. Does refraction occur?
Ans: No.
Some Practical Activities or Situations Related to Refraction
- Place a glass slab on the letters in a textbook. The letters appear raised.
- Difficulty in taking a coin lying under the water in a trough by looking through any one side of the trough.
- The bottom of a pond appears elevated when viewed from a distance than from a nearer point.
- People who engage in bow fishing aim at a point slightly below the perceived position of the fish.
Atmospheric Refraction
Why do stars at a greater distance twinkle?Stars appear as point sources of light because they are at a greater distance from the Earth compared to the planets. The light coming from the stars reaches our eyes by traversing through the atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere consists of several layers, and the refractive index of each layer varies due to variations in temperature and pressure. Hence, the light undergoes an irregular refraction. Therefore, when the light rays from the stars reach the eyes after several refractions, the star cannot be seen continuously at the same position. This is the reason for the twinkling of stars.
Even after the Sun has passed the western horizon, the Sun is visible for some more time. Similarly, the Sun can be seen a few seconds before it reaches the eastern horizon in the morning. What is the reason?

Total Internal Reflection
Allow light from a laser torch to fall at different angles on the surface of water taken in a trough.
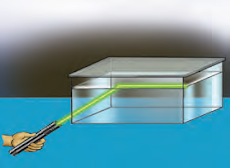

Which are the mediums through which light passes inside the trough?
The light travels from water to air inside the trough.
Does the light enter from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium or from an optically rarer medium to a denser medium?
The light enter from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium
Increase the angle of incidence gradually. What do you observe?
The angle of refraction goes on increasing with the increase in the angle of incidence. The incident ray reflects back to the water completely when the angle of incidence is above a specific value.
Try out an experiment.


From which medium to which does the ray of light enter? (from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium / from an optically rarer medium to a denser medium)
Ans: From an optically denser medium to a rarer medium
What is the change in the angle of refraction when the angle of incidence increases?
Ans: The angle of refraction goes on increasing with the increase in the angle of incidence.
What is the angle of incidence when the angle of refraction is 90⁰?
Ans: Angle of refraction = 42⁰
What peculiarity do you notice when the light is incident at an angle greater than this angle of incidence?
Critical Angle
When a ray of light enters from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium, the angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction becomes 90⁰ is the critical angle. In the glass-air pair, the critical angle is 42⁰.
Total Internal Reflection
When a ray of light enters from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium, at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, the ray is reflected back completely to the same medium without undergoing refraction. This phenomenon is total internal reflection.
The path of light through different mediums is given. Analyse the figures and answer the following questions.

a) Which of the above figures represent total internal reflection?
Ans: Figures 'a' and 'e'
b) What is the critical angle of glass in this case?
Ans:42⁰
c) Will total internal reflection occur for a ray of light entering from water to air at an angle of 50⁰? Why? What is the critical angle for the water-air pair?
Ans: Yes, because the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. The critical angle of water-air pair is 48.6⁰
d) What are the two conditions required for total internal reflection to occur?
(i) Light should be travelling from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium.
(ii) The angle of incidence should be greater than critical angle.
The bottom of the aquarium is seen above the surface of water. What may be the reason?
The light coming from the bottom of the aquarium undergoes total internal reflection at the surface of water. Hence, the bottom is seen above the surface of water.
During summer season there seems to be water logging on roads when viewed from a distance. What may be the reason?
The layers of air closer to the road have a low optical density as it is warmer than the upper layers. The optical density of the air increases gradually as we go higher.
When light rays coming from the surrounding objects pass through different layers of air with different optical densities, they undergo refraction and then total internal reflection. Such deviated light rays fall on our eyes. Hence their image appears to have formed on roads. This phenomenon is known as mirage.
Applications of Total Internal Reflection
i)Reflectors in vehicles

A large number of small prisms are fixed inside the reflectors. A ray of light that incidents on a prism get reflected, this is depicted in the figure given below.

The light ray is incident normally on the side PQ. Hence, there is no refraction. The critical angle of glass is 42⁰. The angle of incidence at A and B is 45⁰. Hence the light falling on A undergoes total internal reflection and reaches B. There it undergoes total internal reflection again and comes out of the reflector as shown in the figure. The same process happen in other prisms in the reflector as well.
ii)Periscope
Periscopes are also made using prisms to increase visual clarity.

iii) Optical Fibre
The invention of optical fibres brought about revolutionary changes in the field of telecommunications. Total internal reflection of light is made use of in optical fibre cables (OFC). Based on this phenomenon, communication signals (optical signals) also travel through optical fibres in the form of light rays.
Thousands of optical signals can be sent simultaneously through a single cable without the loss of intensity. Such signals can be sent to distant places with the speed of light. This is the reason for using optical fibre cables in communication.
Statements regarding total internal reflection and reflection from plane mirror are given. Tabulate them suitably.

Let's Assess
1) Ray diagram showing the path of light through mediums A and B is given.

a) In which medium will the speed of light be less A or B ?
Ans: Medium B
b) Which will be the optically denser medium? Justify your answer.
Ans: B is the optically denser medium, because the ray of light deviates towards the normal while traveling from A to B. This clearly indicates that the optical density of medium B is more than that of medium A.
2. Complete the given diagram. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of refraction.

3. Light passes from medium X to Y.
Here, the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence.
a) In which medium is the speed of light more?
Ans: Medium Y
b) Which is the medium of larger refractive index?
Ans: Medium X
c) Draw the path of light.

4. Refractive index of different mediums are given in the table.

Ans: Water
b) Will a ray of light entering obliquely from glycerine to sunflower oil deviate? Explain the reason.
Ans: No, because they have the same refractive index.
c) Light is transmitted from glass to each medium listed in Table. If light is incident at an angle of 30⁰, which medium will have the largest angle of refraction? Why?
Ans: Water. Refractive index of glass is 1.5 and that of water is 1.33. Here the light is travelling from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium therefore the angle of refraction will be greater than the angle of incidence. As refractive index decreases angle of refraction increases
5. Observe the figure. Ray of light incident on two mediums is depicted.

a) Which is the medium of higher optical density? Why?
Ans: Medium 1, because as optical density increases the angle of refraction decreases.
b) Which is the medium of greater refractive index?
Ans: Medium 1
6. Observe the figures.

a) Which figure indicates total internal reflection?
Ans: Figure (a)
b) Which figures indicate refraction?
Ans: Figures (b) and (c)
7. The critical angle of glass is 42⁰. Choose the angle of incidence for which total internal reflection takes place.
a) 40⁰ b) 49⁰ c) 38⁰ d) 42⁰
Ans: 49⁰
8. We can see many small prisms in the reflectors used in motorcycles. Describe the
benefits of using them.
Ans: Small prisms in the reflectors reflect the light effectively and thus other drivers could see the vehicle properly even in dim lights and we can avoid any possibility of accidents.
9. Observe the table.

a) Choose the medium in which light has the least speed.
Ans: Diamond
b) The speed of light in air is 3 x 10⁸ m/s. What is the speed of light in kerosene?

c) When a ray of light enters obliquely from air to diamond, will the refracted ray
deviate towards the normal, or away from the normal? Justify your answer.
Ans: The refracted ray deviate towards the normal. Refractive index of diamond is more than that of air.
10) The path of light through mediums A, B, C and D are given. Choose the correct
figures. (The optical density of the mediums are in the order A<B<C<D)

Ans: Figure (b), figure (d), figure (e)
11. Speed of light in ethanol is lesser than that in methanol. Which medium has lower refractive index? Why?
Methanol has lower refractive index. Mediums having higher refractive index have higher optical density as optical density increases speed of light through the medium decreases.





.png)

.png)

.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)






0 Comments