.png)
1.What type of motion does the swing have?
(circular / oscillatory)
Ans: Oscillatory
Observe the diagram showing the motion of the swing.

2.What is the initial position of the swing when it starts oscillating from its free state (equilibrium position)? (A / O / B)
Ans: O
3.In the figure, what is the maximum displacement to one side from the equilibrium position? (2a, a/2 , a)
Ans: a
4.When does the swing complete one oscillation?
(when the pendulum starts from O, reaches A and returns to O / when the pendulum starts from O, reaches A, then to B and back to O)
Ans: When the pendulum starts from O, reaches A, then to B and back to O
5.The frequency of a simple pendulum is 1 Hz. What is its period?
Ans:
Frequency(f) = 1/Period(T)= 1/1 = 1s
6.If a pendulum takes 0.5 s to complete one oscillation, what is its frequency?
Ans:
T = 0.5s
f = 1/T
= 1/0.5
= 2Hz
7.A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is excited and its stem is pressed on a table. Does the table vibrate in this situation? What is this phenomenon known as?
Ans: Yes, the table vibrates. This phenomenon is known as forced vibration.
8.Some of the characteristics related to transverse waves and longitudinal waves are given below. Classify them and complete the table.
• Particles in the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
• Compressions and rarefactions are formed.
• Pressure variations occur in the medium.
• Crests and troughs are formed.
• Particles in the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave.
• No pressure variations occur in the medium.
Ans:

a) How many crests are there in the figure?
Ans: 3
b) How many troughs are there?
Ans: 3
c) What is the wavelength?
Ans: 8m
10.If the frequency of a longitudinal wave travelling at a speed of 350 m/s in the air is 35 Hz,
a) What is the distance between two consecutive compressions of this wave?
Ans:
The distance between two consecutive compressions of this wave = Wavelength of the wave(λ)
v =350m/s
f = 35Hz
v = f λ
λ = v/f
= 350/35
= 10m
b) What about the distance between two consecutive rarefactions?
Ans:
The distance between two consecutive rarefactions of this wave = Wavelength of the wave(λ)
= 10m
11. A sound wave with a frequency of 175 Hz has a wavelength of 2m. Calculate the speed of sound.
Ans:
f = 175 Hz
λ = 2m
v = f λ
= 175 x 2
= 350m/s
12. What should be the minimum distance between the source and the reflecting surface to hear the echo in water? (Consider the speed of sound in water as 1480 m/s)
Ans:
v = 1480m/s
Total distance travelled by the sound wave to hear echo = speed x time
= 1480 x (1/10)
= 148m
Distance between the source and the reflecting surface = 148/2 =74m
13.Why are the walls of large halls like cinema theatres made rough?
Ans: The walls of large halls, such as movie theaters, are made rough to reduce reverberation, thereby improving sound quality.
14. If an ultrasonic wave emitted by a transmitter, installed on a ship on the surface of the water, strikes a rock at the bottom of the sea and returns after 0.2 s, what is the distance from the ship to the rock? Consider the speed of ultrasonic waves in seawater as 1522 m/s.
Ans:
2d = v x t
d = (1522 x 0.2)/2
d = 152.2 m
Let's Assess
1. Which of the following statements is correct?
a) Sound and light are transverse waves.
b) Sound and light are longitudinal waves.
c) Sound is a longitudinal wave and light is a transverse wave.
d) Sound is a transverse wave and light is a longitudinal wave.
Ans: c) Sound is a longitudinal wave and light is a transverse wave.
2. The upper limit of frequency of sound that a bat can hear is 120 kHz. If so, what is the maximum wavelength of sound it can hear? Consider the speed of sound as 350 m/s.
Ans:
f = 120 kHz = 120000 Hz
v = 350m/s
v = f λ
λ = v/f
= 350/120000
= 0.0029m = 2.9mm
This is the minimum wavelength of sound the bat can hear. [Using the given data we cannot calculate the maximum wavelength of sound the bat can hear]
3. A graphic illustration of two waves travelling at a speed of 3.2 m/s is given.
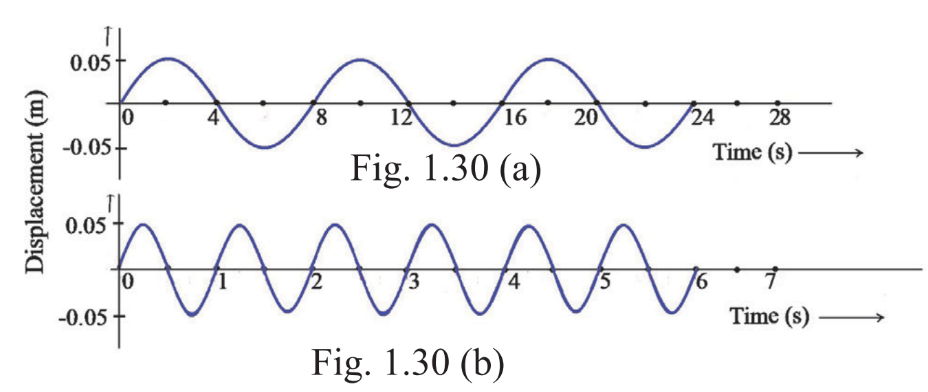
a) Find out the frequency, period, and wavelength of each wave.
Ans:
Fig.1.30(a)
f = No. of waves/ Total time
= 3/24
= 0.125 Hz
T = 1/f
= 1/0.125 = 8s
λ = vT
= 3.2 x 8 = 25.6m
Fig.1.30(b)
T = 1s
f = 1/T =1 Hz
λ = vT
= 3.2 x 1 = 3.2m
4. Which of the following frequency can be heard by humans?
a) 5 Hz b) 2000 Hz c) 200 kHz d) 50 kHz
Ans: b) 2000 Hz
5. A wave has a frequency of 2 kHz and a wavelength of 35 cm. How far does this wave travel in 0.5 s?
Ans:
f = 2 kHz = 2000Hz
λ = 35cm = 0.35m
v = fλ
= 2000x0.35
=700m/s
Distance travelled by the wave in 0.5s = 700 x 0.5
= 350m
6. What is the frequency of a wave that produces 50 crests and 50 troughs in 0.5 s?
Ans: Frequency is the number of waves completed in 1s.
50 crests and 50 troughs together form 50 waves in 0.5s.
therefore, number of waves produced in 1s = 50x2
= 100Hz
Frequency = 100Hz
or
f = No. of waves/time taken
= 50/0.5 = 100Hz
7. Which of the following is different regarding the waves given in the figures 1.31(a) and 1.31(b)? (frequency, amplitude, wavelength)

8. The distance between two adjacent troughs of a transverse wave is 2m. Find the frequency if its speed is 20 m/s.
Ans:
v = 20m/s
λ = 2m
f = v/λ
= 20/2 =10Hz
9.When sound passes through a medium, ................. travels.
(the particles in the medium / the wave / the source of sound / the medium)
Ans: the wave
10.Two pith balls are suspended near the two prongs of a tuning fork fixed on a table so as to touch the prongs. A person plays a piano sitting near this system.
a) In this case the pith balls move slightly. What is the reason? (forced vibration / echo)
Ans: forced vibration
b) While playing certain notes on the piano, the pith balls are thrown to a maximum distance. Which phenomenon is responsible for this? (reverberation / resonance)
Ans: resonance




.png)

.png)

.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)






0 Comments