List the characteristics of concave lenses and convex lenses in the table.

Ray Diagram of the Image Formation by a Convex Lens
A ray of light passing parallel to the optic axis incident on a convex lens




Object at 2F

Object between 2F and F

Object at F

Object between F and the lens

Position of the image: On the same side of the object
Characteristics of the image: Erect, Magnified, Virtual
Image Formation by a Concave Lens
Ray diagram of image formation by concave lens


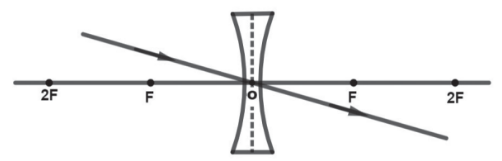

Position of the image: Between F and the lens
Characteristics of the image: Erect, Diminished, Virtual

Position of the image: Between F and the lens
Characteristics of the image: Erect, Diminished, Virtual
A concave lens has a focal length of 20 cm. An object of height 2 cm is placed at a distance 30 cm from the lens on the optic axis.
a) Calculate the distance from the lens to the image.
b) How much will the magnification be? What are the characteristics of the image?
Ans:
a)


b)

Let's Assess
1. The focal length of a convex lens is 20 cm. An object of height 3 cm is located at a distance of 60 cm from its optic centre on the optic axis.
a) Calculate the height of the image.
b) What are the characteristics of the image obtained?
a)




a) An object is placed 30 cm away from the lens. Calculate how far the screen should be placed to get a clear image.
b) If the height of the object is 1.2 cm, what will be the height of the image appearing on the screen?
Ans:
Since the image is formed on a screen, it is a real image. Therefore the lens is a convex lens.
f = 20cm
u = -30cm




An inverted image of 2.4cm is formed on the screen.
3. The focal length of a convex lens is 100 mm. An object of height 15 mm is located 60 mm from the optic centre on its optic axis.
a) Draw its ray diagram on a graph paper and find the position and height of the image.
b) Calculate the magnification if the distance to the object is 20 mm.
Ans:
a) An image of height about 37.5mm is formed at a distance of 150mm from the optic axis on the same side as that of the object.
b) f = 100mm
u = -20mm


4. Four statements are given regarding the image formed by a concave lens. Find and choose the correct answer.
i. It will be diminished and inverted
ii. It will be diminished and virtual
iii. It will be magnified and virtual
iv. It will be diminished and erect
a) Only the second statement is true
b) Only the first statement is true
c) Second statement and fourth statements are true
d) Only the third statement is true
Ans: c) Second statement and fourth statements are true
5. A concave lens has a focal length of 50 cm. What will be its power?
a) +2 D b) +0.5 D c) −2 D d) −0.5 D
Ans: -2D
Hints:
f = -50cm = -0.5m
P = 1/f
6. Find the most appropriate statement related to a telescope.
a) The objective lens has a shorter focal length and the eyepiece lens has a longer focal length.
b) The objective lens has a longer focal length and the eyepiece has a shorter focal length.
c) Objective lens and eyepiece lens are concave lenses.
d) Objective lens will be concave lens and eyepiece lens will be convex lens.
Ans: b) The objective lens has a longer focal length and the eyepiece has a shorter focal length.
7. When an object is placed in front of a lens, the image formed is inverted.
a) Is it real or virtual?
b) What will you do if you want another image of this obtained image to be real, erect and of the same size?
Ans:
a) Real
b) An another convex lens is to be placed in such a way that the image formed by the first lens is at the 2F of the second lens.
8. When an object is placed at the principal focus of a lens, an image that is erect and diminished is obtained.
a) What kind of lens is this?
b) Draw the ray diagram of the image formation.
Ans:
a) Concave
b)

9. The image (IM) obtained when an object is placed in front of a lens is depicted.

a) If PQ is a lens in the figure, what type of lens does PQ represent?
b) Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the object.
c) The height of the object is ........ than the height of the image (greater / lesser).
Ans:
a) Convex
b)
Object is in between 2F and F.
c) lesser
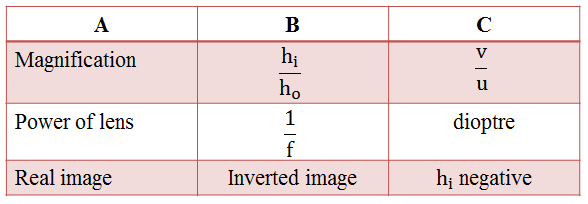
10. Match the items in the columns A, B and C appropriately.

Ans:


.png)


.png)

.png)

.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)






0 Comments